Understanding the Meaning of RPM on a Car
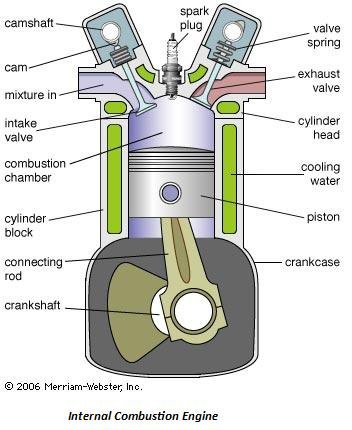
When you drive a car, you may notice a gauge on the dashboard that displays RPM. But what does RPM actually mean? RPM stands for “revolutions per minute” and it is a measurement of how many times the engine’s crankshaft completes a full rotation in one minute. In other words, RPM tells you how fast the engine is spinning.
RPM is an important indicator of an engine’s performance. It can give you insight into how hard the engine is working and how much power it is producing. For example, a higher RPM generally means that the engine is producing more power and is working harder. On the other hand, a lower RPM indicates that the engine is running at a slower speed and may not be operating at its full potential.
RPM is often used by drivers to determine when to shift gears in a manual transmission car. Each gear has an optimal RPM range in which it operates most efficiently. Shifting gears outside of this range can result in decreased fuel efficiency and potential damage to the engine. By paying attention to the RPM gauge, drivers can make more informed decisions about when to shift gears, which can improve overall driving performance.
Understanding RPM in Cars: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to understanding how a car engine works, one of the key concepts to grasp is RPM, or revolutions per minute. RPM refers to the speed at which the engine’s crankshaft is rotating. It is a crucial metric that provides insight into the performance and functioning of a car.
In simple terms, RPM indicates the number of times the crankshaft completes a full rotation in one minute. This rotation is essential for various engine components, such as the pistons, valves, and camshaft, to function correctly.
Knowing the RPM of a car is vital for several reasons. First and foremost, it helps drivers understand the engine’s power and torque capabilities. Higher RPM values generally indicate a more powerful engine, as it can rotate at a faster speed. On the other hand, lower RPM values might suggest a less powerful engine.
Furthermore, RPM is crucial when it comes to gear shifting. It helps drivers determine the optimal time to shift gears for fuel efficiency and performance. Each gear has a specific range of RPM within which it is most effective. Shifting gears at the right RPM can ensure a smooth and efficient driving experience.
RPM is also relevant for maintaining the overall health of an engine. Reaching extremely high RPM levels for an extended period can strain the engine and lead to overheating or other mechanical issues. Monitoring and controlling RPM allows drivers to keep the engine running within safe limits.
Modern cars typically have a tachometer, a gauge that displays the RPM, to help drivers keep track of their engine’s speed. The tachometer is usually located on the dashboard, alongside other essential gauges such as speedometer, fuel gauge, and temperature gauge.
In conclusion, understanding RPM is vital for car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike. It provides critical information about the engine’s power, gear shifting, and overall health. By paying attention to RPM, drivers can make informed decisions that optimize their driving experience and ensure the longevity of their vehicles.
What Is RPM and How Does It Affect Your Car’s Performance?
RPM stands for revolutions per minute, and it is a measurement of how many times the engine’s crankshaft completes a full rotation in one minute. It is an important factor in determining the performance of your car as it directly affects the engine’s power output.
Understanding RPM
The RPM gauge, also known as a tachometer, is a display that shows the current engine speed in revolutions per minute. It is usually located on the dashboard of a car and is marked with numbers ranging from 0 to 6 or 8 thousand RPM, depending on the car model.
When you start your car, the RPM gauge will typically show a reading of around 700 to 1000 RPM. This is the idle speed, which is the speed at which the engine is running when it is not under load. As you press the accelerator pedal, the RPM will increase gradually, meaning the engine is working harder and rotating faster.
Impact on Performance
The RPM plays a crucial role in determining the performance capabilities of your vehicle. Generally, higher RPMs result in increased power output. This means that the engine is rotating faster, allowing it to produce more power to propel the car forward.
However, it is important to note that each car has a specific RPM range where it operates most efficiently. This range, often referred to as the power band or peak torque range, is typically mentioned in the car’s specifications. Operating the engine within this range optimizes power delivery and fuel efficiency.
When the engine operates at too low of an RPM, it may struggle to generate enough power, resulting in decreased acceleration and overall performance. On the other hand, running at excessively high RPMs for an extended period can put a strain on the engine and reduce its lifespan.
Furthermore, the transmission of a car plays a significant role in managing RPMs as it determines the gear ratio. Shifting gears at the correct RPM range allows the engine to stay within its optimal operating range, further enhancing performance and fuel economy.
In conclusion, RPM is a key factor in your car’s performance. Understanding how it affects engine power output and operating within the recommended RPM range can help you maximize your car’s performance while ensuring its longevity.
The Relation Between RPM and Engine Speed: Explained
RPM, which stands for revolutions per minute, is a measure of how fast the engine’s crankshaft is rotating. It indicates the number of complete revolutions the crankshaft is making in a minute. Engine speed, on the other hand, refers to how fast the engine is running in terms of rotations per minute.
RPM and engine speed are closely related because RPM directly reflects the engine speed. When the RPM is high, it means the engine is running at a higher speed, and when the RPM is low, it indicates a lower engine speed.
The RPM can vary depending on various factors such as the gear the vehicle is in, the throttle position, and the load on the engine. For example, when you shift to a higher gear, the RPM tends to decrease because the engine doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain the same speed. Conversely, when you shift to a lower gear or press the accelerator pedal, the RPM increases as the engine has to work harder to produce more power.
Monitoring the RPM is crucial because it helps drivers understand the engine’s performance and efficiency. By keeping an eye on the RPM, drivers can determine the appropriate shifting points, avoid overrevving the engine, and ensure optimal fuel consumption. Manufacturers often provide a recommended RPM range for each gear to maximize performance and fuel efficiency.
In conclusion, RPM and engine speed are interconnected, with RPM being a measure of the engine’s rotational speed. Understanding this relationship can assist drivers in optimizing their driving experience and taking care of their vehicles.
Why Monitoring RPM is Essential for Efficient Driving
When it comes to driving a car, monitoring the RPM (Revolutions Per Minute) is essential for maintaining efficient and optimal performance. RPM refers to the number of times the engine’s crankshaft completes a full rotation in one minute. By monitoring the RPM, drivers can effectively manage their speed, fuel consumption, and overall driving experience.
Optimal Shift Points
One of the key benefits of monitoring RPM is the ability to determine the optimal shift points. Each vehicle has a specific RPM range in which it operates most efficiently. By keeping an eye on the RPM gauge, drivers can identify these range boundaries and shift gears accordingly. Shifting too early or too late can result in increased fuel consumption and decreased performance.
When the RPM is too low, it signifies that the engine is struggling to produce enough power. This may occur when attempting to accelerate in a high gear or climbing a steep incline. By downshifting and bringing the RPM up to its optimal range, drivers can ensure that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
On the other hand, excessively high RPM indicates that the engine is working too hard, which can lead to increased wear and tear. By shifting up to a higher gear, drivers can reduce the RPM and achieve a more fuel-efficient driving experience.
Fuel Efficiency
Monitoring RPM is crucial for achieving optimal fuel efficiency. By maintaining an appropriate RPM range, drivers can minimize unnecessary fuel consumption. When the RPM is too high, the engine burns more fuel to produce power. Conversely, when the RPM is too low, the engine may struggle to operate efficiently. By staying within the recommended RPM range, drivers can strike a balance between power and fuel consumption.
Additionally, monitoring RPM can help drivers identify patterns and adjust their driving habits to maximize fuel efficiency. By learning to anticipate gear shifts and optimizing acceleration and deceleration, drivers can significantly reduce fuel consumption and contribute to a more sustainable driving experience.
Conclusion
Monitoring RPM is essential for efficient driving. By understanding the optimal RPM range, drivers can ensure smooth gear shifts, minimize fuel consumption, and extend the lifespan of their vehicles. By paying attention to the RPM gauge and making adjustments as needed, drivers can enjoy a more economical and enjoyable driving experience.
How RPM Impacts Fuel Efficiency: Key Factors to Consider
When it comes to fuel efficiency, the revolutions per minute (RPM) of a car can play a significant role. RPM refers to the number of times the engine’s crankshaft rotates in a minute. Understanding how RPM affects fuel efficiency can help car owners make informed decisions to save on fuel costs.
Here are some key factors to consider regarding how RPM impacts fuel efficiency:
| RPM Range | Fuel Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Low RPM | High |
| Mid RPM | Optimal |
| High RPM | Low |
1. Low RPM: Running the engine at low RPM can lead to high fuel efficiency. This is because the engine is operating at a slower pace, requiring less fuel to maintain the same speed. However, low RPM can result in less power and slower acceleration.
2. Mid RPM: Maintaining the engine at mid RPM can optimize fuel efficiency. This range allows the engine to produce enough power while still conserving fuel. It provides a good balance between performance and economy.
3. High RPM: Operating the engine at high RPM can significantly decrease fuel efficiency. This is because the engine is working harder, consuming more fuel to generate more power. High RPM is often needed for quick acceleration or climbing steep hills, but it should be avoided for regular driving to save on fuel costs.
Other factors that can affect fuel efficiency include driving habits, vehicle weight, aerodynamics, and the condition of the car’s components. Aggressive driving with frequent and rapid accelerations can reduce fuel efficiency, regardless of the RPM range. Additionally, carrying excess weight in the car or having poor aerodynamics can increase fuel consumption.
In conclusion, while RPM is an important factor that can impact fuel efficiency, it should be considered alongside other variables. Finding the right balance between RPM and driving conditions can help maximize fuel efficiency and save on costs in the long run.
RPM and Engine Lifespan: Tips for Maintaining Optimal Performance
Understanding RPM, or revolutions per minute, is essential for maintaining the longevity and performance of your car’s engine. The RPM gauge on your dashboard indicates the number of times the engine’s crankshaft rotates in one minute. Monitoring and managing RPM levels can help ensure that your engine remains in good condition and performs optimally.
Excessive RPM can put an unnecessary strain on your engine, leading to accelerated wear and tear. It’s important to avoid consistently running your engine at high RPMs for extended periods, as this can result in overheating and potential damage. Likewise, operating your engine at low RPMs for prolonged periods can lead to poor lubrication and performance issues.
To maintain optimal RPM levels and prolong your engine’s lifespan, follow these tips:
- Observe recommended RPM range: Every car has a specific RPM range within which it operates best. Consult your vehicle’s manual or contact the manufacturer to determine the ideal RPM range for your engine. It’s important to avoid pushing your engine’s RPM beyond this range to prevent unnecessary strain.
- Shift gears smoothly: Proper gear shifting is crucial for maintaining engine RPM within the recommended range. Avoid harsh acceleration or abrupt gear changes, as these can lead to sudden RPM spikes. Instead, shift gears smoothly and gradually to keep RPM levels stable.
- Regular maintenance: Keeping up with regular maintenance tasks such as oil changes, spark plug replacements, and air filter cleanings is vital for optimal engine performance. Dirty oil, worn-out spark plugs, and clogged air filters can adversely affect RPM and engine efficiency. Consult your vehicle’s manual for recommended maintenance schedules.
- Monitor RPM gauge: Pay close attention to your car’s RPM gauge while driving, especially during acceleration and deceleration. If you notice abnormal RPM fluctuations or sustained high RPM levels, it may indicate a potential issue with your engine that requires attention from a qualified mechanic.
- Avoid unnecessary idling: Extended idling not only wastes fuel but also puts additional strain on your engine. When possible, avoid leaving your car idling for extended periods. It’s better to turn off the engine and restart it when needed.
By following these tips and maintaining optimal RPM levels, you can prolong the lifespan of your car’s engine and enjoy reliable performance for years to come.
Using RPM to Shift Gears: Mastering the Art of Shifting
Shifting gears is an essential skill for any driver, especially when driving a manual transmission car. But what exactly does RPM have to do with shifting? RPM, or revolutions per minute, refers to the speed at which the engine is rotating. Understanding how to use RPM to shift gears can greatly improve your driving experience and even extend the life of your vehicle.
The Basics of Shifting
Before we dive into the details of using RPM to shift gears, it’s important to understand the basics of shifting. In a manual transmission car, there are typically five or six gears, labeled with numbers on the gear stick. Each gear has a specific purpose and is designed to be used at different speeds. Shifting gears allows you to match the engine’s RPM with the speed of the vehicle, ensuring smooth and efficient acceleration.
The Role of RPM
RPM plays a crucial role in determining when to shift gears. As you accelerate, the RPM will increase, indicating that the engine is revving faster. Each gear has a specific range of RPMs in which it operates optimally. It’s important to pay attention to the RPM gauge on your dashboard and shift gears accordingly to keep the engine operating within its ideal range.
When shifting, you want to avoid shifting too early or too late. Shifting too early can cause the engine to struggle and lose power, while shifting too late can put excessive strain on the engine. The goal is to find the sweet spot where the engine is revving efficiently without overexerting itself.
Downshifting and Upshifting
When shifting gears, there are two main techniques: downshifting and upshifting. Downshifting involves shifting to a lower gear, allowing the engine to run at a higher RPM. This technique is commonly used when slowing down or preparing to accelerate, as it provides more power and control. Upshifting, on the other hand, involves shifting to a higher gear, allowing the engine to run at a lower RPM. This technique is used when you’re already at a high speed and want to improve fuel efficiency.
Mastering the Art of Shifting
Mastering the art of shifting takes practice and experience. As you become more familiar with your car’s RPM range, you’ll learn to anticipate when to shift gears based on the sound and feel of the engine. It’s important to be smooth and deliberate when shifting, using a gentle yet firm hand to change gears. Proper gear shifting not only improves your driving experience but also helps to prolong the life of your transmission and engine.
In conclusion, RPM is a crucial factor when it comes to shifting gears in a manual transmission car. By understanding how to read the RPM gauge and using the appropriate techniques for downshifting and upshifting, you can ensure a smooth and efficient driving experience.
Understanding RPM Limiters and Redlining: Dos and Don’ts
When it comes to understanding RPM (revolutions per minute) limiters and redlining, there are some important dos and don’ts to keep in mind. RPM limiters are electronic devices or software that prevent a car’s engine from exceeding a certain speed or rotational speed. Redlining, on the other hand, refers to revving the engine to its maximum RPM.
Here are some dos and don’ts when it comes to RPM limiters and redlining:
1. Do understand your car’s RPM limiter: Every car has a specific RPM limiter set by the manufacturer. It is important to know this limit and not exceed it to avoid engine damage or failure. Exceeding the RPM limiter could cause overheating, excessive wear and tear on the engine components, and potential engine failure.
2. Don’t constantly redline your engine: While redlining might seem thrilling, it is not recommended to do it regularly. Continuously revving your engine to its maximum RPM can put excessive stress on the engine, leading to premature wear and tear, reduced engine lifespan, and potential damage.
3. Do consider the engine’s operating range: Each engine has a specific operating range where it performs optimally. It is important to understand this range and avoid pushing the engine beyond its capabilities. Running the engine at extremely high RPMs for prolonged periods can cause unnecessary strain and damage.
4. Don’t ignore warning signs: If your car’s RPM limiter kicks in or you notice any unusual sounds, vibrations, or performance issues, it’s important not to ignore these warning signs. They could indicate a problem with the engine, such as a malfunctioning RPM limiter or potential mechanical issues. It is advisable to have your car inspected by a professional if you encounter any concerning symptoms.
5. Do practice responsible driving habits: Instead of constantly redlining your engine, focus on practicing responsible driving habits. This includes shifting gears at appropriate RPM levels, maintaining regular engine maintenance and servicing, and avoiding unnecessary strain on the engine. By driving responsibly, you can ensure the longevity and performance of your car’s engine.
Overall, understanding RPM limiters and redlining is crucial for maintaining the health of your car’s engine. By following the dos and don’ts mentioned above, you can avoid potential damage and ensure the longevity and performance of your vehicle.
How to Improve RPM Response: Performance Upgrades and Tuning
If you’re looking to improve the RPM response of your car, there are several performance upgrades and tuning options available to enhance its performance. These modifications can help your car achieve higher RPMs more efficiently and provide a more exhilarating driving experience.
1. Cold Air Intake
One of the most common and effective upgrades to improve RPM response is installing a cold air intake. This modification allows your car’s engine to breathe in cooler air, which is denser and contains more oxygen. With the increased oxygen supply, your engine can combust fuel more efficiently, resulting in better RPM response.
2. Performance Exhaust System
Upgrading your car’s exhaust system can also improve RPM response. A high-performance exhaust system allows for better airflow, reducing back pressure and improving the engine’s efficiency. This enhancement can lead to improved RPMs and a more aggressive sound.
Additionally, a performance exhaust system can help your engine expel exhaust gases more efficiently, which may result in increased power and overall performance.
3. Performance Tuning
Another way to improve RPM response is through performance tuning. This involves adjusting various parameters of your car’s engine control unit (ECU) to optimize its performance. Performance tuning can include modifying fuel maps, ignition timing, and throttle response, among other things.
By fine-tuning these settings, you can improve RPM response and overall engine performance. However, it’s essential to consult with a reputable tuner or use specialized tuning software to ensure the modifications are done safely and effectively.
Remember that each car is unique, and the specific upgrades and tuning options that work best will depend on your vehicle’s make, model, and engine type. It’s always a good idea to research and consult with automotive professionals before making any significant modifications to your car.
In conclusion, if you want to improve RPM response, consider performance upgrades such as a cold air intake and performance exhaust system, along with performance tuning. These modifications can help your car achieve higher RPMs more efficiently, providing a more exciting driving experience.
Question-Answer:, What does rpm mean on a car
What is RPM?
RPM stands for revolutions per minute. It is a unit of measurement used to describe the rotational speed of a car’s engine.
Why is RPM important?
RPM is important because it indicates how fast the engine is rotating. It helps the driver in determining when to shift gears and provides a measure of the engine’s performance.
How does the RPM affect fuel consumption?
Higher RPM generally leads to higher fuel consumption. This is because the engine is working harder and using more energy to rotate at a faster speed. Keeping the RPM within a reasonable range can help improve fuel efficiency.
What can cause high RPM?
There are several possible causes for high RPM, including a malfunctioning sensor, a problem with the throttle body, or a faulty transmission. It is best to have the car inspected by a mechanic to determine the exact cause of the high RPM.